USHA VACCINATION
Vaccinations save lives, Prevent diseases, and ensure a healthier future for everyone. Get vaccinated today.
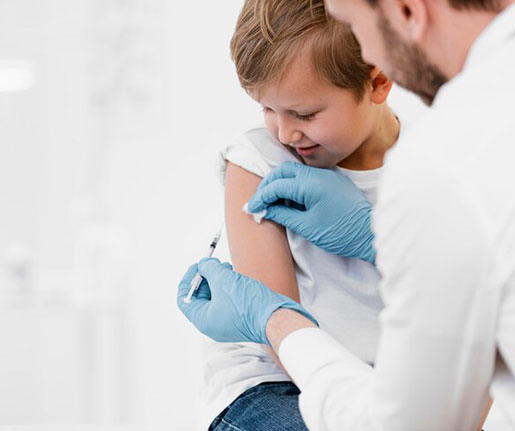
Here are some key suggestions to ensure a smooth recovery and maintain your health:
Take It Easy: Allow yourself to rest, especially if you feel tired. Avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day.
Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support your body's recovery process.
Soreness: Mild redness, swelling, or soreness at the injection site is normal. Applying a cool compress can help ease discomfort
Fever: A slight fever can occur. Stay hydrated and rest, and use over-the-counter medications if necessary.
Fatigue and Aches: If you experience fatigue or muscle aches, these are usually temporary. Rest and over-the-counter pain relievers can help.
Watch for Severe Reactions: Rarely, more serious side effects may occur, such as difficulty breathing or severe allergic reactions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
Track Your Symptoms: If side effects persist or worsen over a few days, consult your healthcare provider.
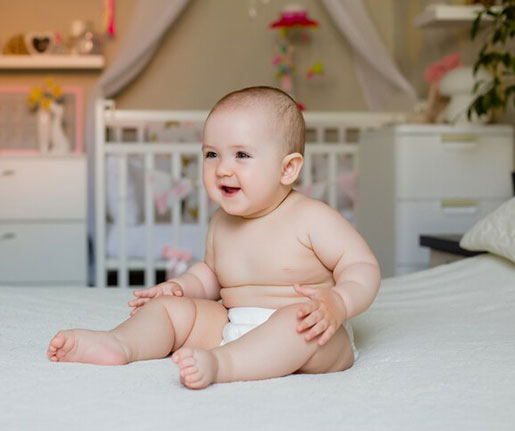

Schedule Follow-Up Appointments: If your vaccine requires additional doses or boosters, be sure to keep track and attend these appointments.
Keep Your Vaccination Records: Maintain a record of your vaccinations for future reference and health needs.
Increased Risk of Disease: Without vaccination, you are more susceptible to preventable diseases, which can lead to severe illness or complications.
Disease Outbreaks: Delays can contribute to outbreaks, as unvaccinated individuals can spread diseases to others.
Long-Term Health Implications: Missing vaccines can result in longer-term health issues, including chronic complications from diseases that could have been prevented.
Higher Healthcare Costs: Treating diseases that could have been prevented by vaccination often leads to higher medical costs and more extensive treatments.

Call us if you have any problems.
Vaccines protect your baby from serious and potentially life-threatening diseases. They help build immunity and reduce the risk of outbreaks, ensuring your baby stays healthy and safe.
Most vaccines are given starting at birth, with a schedule of immunizations recommended during the first year of life. Your pediatrician will provide a timeline for each vaccine.
Common vaccines in the first year include those for hepatitis B, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), polio, rotavirus, and pneumococcal disease.
Yes, vaccines are rigorously tested for safety and effectiveness. Side effects are generally mild, such as soreness at the injection site or a slight fever. The benefits far outweigh any potential risks.
Common side effects include mild soreness, fever, or irritability. You can manage these by using a cool compress, keeping your baby hydrated, and administering over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen, as advised by your pediatrician.
Contact your healthcare provider to reschedule the missed vaccine. It's important to complete the vaccination series to ensure full protection.
Some vaccines are not given during infancy, such as those for certain diseases that are more common in older children or adults. Your pediatrician will provide guidance on which vaccines are appropriate for your baby's age and health.
No, vaccines are designed to prevent serious diseases and have a strong safety record. Long-term health issues related to vaccines are extremely rare compared to the risks of the diseases they prevent.
Keep track of your baby's vaccination schedule with the help of your pediatrician. They will provide reminders and ensure that your baby receives all necessary vaccines on time.
For more information, visit ( url ) Information page or speak with your pediatrician for personalized advice.
Vaccinations are one of the most effective tools in preventing serious and often life-threatening diseases. Understanding vaccine-preventable diseases helps you make informed decisions about your health and the health of your loved ones. This guide provides an in-depth look at common vaccine-preventable diseases, their impacts, and how vaccines help prevent them.